Questions similar to these appear in the Be Communities MicroStation Programming Forum.
This page lists some solutions to common MicroStation VBA (MVBA) problems. Tips are published as examples and are not necessarily working code.
Text Search Tool
We've created a text search & replace tool for MicroStation, written in MicroStation VBA. You can search for text in several different element types, and you can use a regular expression if required.
You don't need to know anything about VBA or regular expressions (RegEx or RE) to use our tool. If you're not interested in the description of the VBA code that follows, then skip to the download section.
Why Replace MicroStation's Built-In Tool?
Q MicroStation already has a text search-and-replace tool. Why write another?
A Good question! There are three reasons. MicroStation's built-in text search tool …
- Offers a rather primitive version of regular expression (RE) matching. This VBA implementation uses a more up-to-date RE algorithm
- Does not permit a regular expression for the replacement text. In contract, this tool allows either a simple text replacement, or a complex substitution using regular expression groups
- Is a black box: this article describes a VBA implementation for which source code is provided. VBA dabblers can dabble!
ECMAScript® Language Specification
MicroStation CONNECT's regular expression engine uses ECMAScript syntax. That's a more advanced engine than was available for previous versions of MicroStation.
Example Regular Expressions
Search for CH123 or CH 123
Here's an example RegEx: [A-Z]{2} ?[0-9]{3}
The expression is designed to …
| Components | Meaning | Matches |
|---|---|---|
[A-Z]{2} | Match exactly two upper-case characters | CH |
? | Match an optional space (there's a space before the ?) | |
[0-9]{3} | Match exactly three digits | 123 |
That expression matches strings such as CH123 and CH 123.
Search for 123456 and replace with 123+456
In other words, split the text in two and reassemble it with a plus sign in the middle. We solved that with a regular expression to find the six-digit string and another regular expression to create the required result.
The search expression is ^([0-9]{3})([0-9]{3})$. It means: find two groups of exactly three digits,
one at the beginning of the text and one at the end. Each group is saved for use in the replacement expression.
Breaking that down to make it easier to understand:
regular expression [0-9]{3} mean find exactly three ({3}) digits ([0-9]).
^ means start at the beginning of the text.
Wrapping the expression in parenthesis specifies a capture group that is used later.
So ^([0-9]{3}) instructs the expression engine to capture a group (Group 1) of three digits at the beginning of the text.
$ means look at the end of the text.
So ([0-9]{3})$ instructs the expression engine to capture another group (Group 2) of three digits at the end of the text.
The replace expression is $1+$2.
$1 and $2 mean Group 1 and Group 2.
We're saying: the replacement text is the contents of Group 1 followed by a plus sign and then the contents of Group 2.
So 123456 is replaced with 123+456, or 104400 is replaced with 104+400.
Unicode
Visual Basic for Applications (VBA), which evolved from VB 5½, has limited support for string manipulation. For example, a MicroStation user wanted to detect a Unicode character in a text string like this …
Area = 100m\178
178 is Unicode for a superscript figure two (like this ²).
User wants to create text in MicroStation that looks like this …
Area = 100m²
The Problem
The problem we want to solve, that VBA makes it hard to do, is to search a String for a sequence of
characters like \178 so that we can substitute an alternative.
More generally, you ask: “How can we search a String for an arbitrary sequence of
characters, and then replace those characters?”
Labour Intensive Solution
The hard way to solve this problem is to write code using VBA's string functions.
Those include Left, Right, InStr, StrComp etc.
You end up writing some convoluted code that solves a particular problem but is difficult to generalise …
Sub ExampleStringHack ()
Const example As String = "Area = 100m\178"
Dim pos As Integer
pos = InStr (example, "\")
Dim s1 As String
s1 = Left (example, pos - 1)
Dim code As String
code = Mid (example, pos + 1, 3)
Dim s2 As String
s2 = Mid(example, pos + 4)
Dim result As String
result = s1 & Chr$(CInt (code)) & s2
Debug.Print "result=" & result
End Sub
Regular Expression Solution
Regular expressions (also known as RegEx or just RE) were invented to help solve the above sort of problem. Regular expressions let you write a very precise search rule. Depending how it's implemented, a RegEx engine lets you make substitutions.
Unfortunately, VBA does not include a RegEx engine. You'll have to borrow one. Fortunately, Microsoft provides one in the form of a COM plug-in. Originally developed for VBScript, this COM server works just as well for VBA. Its name — take a deep breath — is Microsoft VBScript Regular Expressions 5.5. It's been around for a few years, and is probably already installed on the PC you are using.
To use Microsoft VBScript Regular Expressions 5.5, you must first make a VBA reference to it …
- Choose the Tools|References menu in the VBA IDE menu bar
- The References dialog opens
- Scroll down the list of available COM servers to find Microsoft VBScript Regular Expressions 5.5
- The list is long
- Check the box alongside Microsoft VBScript Regular Expressions 5.5
- You can now use the objects from Microsoft VBScript Regular Expressions 5.5

Regular Expression Objects
Press F2 with the VBA IDE open to see available object libraries. Choose VBScript_RegExp_55 to see the four objects provided by the DLL …
-
RegExp -
Match -
MatchCollection -
SubMatches
You can find more about Microsoft VBScript Regular Expressions 5.5 through a web search. For example, How To Use Regular Expressions in Microsoft Visual Basic.
A Regular Expression to find a Unicode Sequence
Here's a regular expression that will find a sequence of characters such as \178 …
\\[0-9]{3,4}
What that means is: "Find a sequence of three or four digits preceded by a backslash". Once we find that sequence in a string, we want to extract it and substitute the Unicode character. Here's the VBA code to convert that sequence into a single character …
' --------------------------------------------------------------------- ' ConvertUnicodeToChar ' 'code' is a string such as '\178' ' Returns: Character corresponding to code e.g. ² ' --------------------------------------------------------------------- Function ConvertUnicodeToChar(ByVal code As String) As String Dim unicode As Integer ' Step over backslash and get numeric value e.g. 178 unicode = CInt(Mid(code, 2)) ' Convert numeric value to Unicode character ConvertUnicodeToChar = Chr$(unicode) End Function
The following subroutine uses the Microsoft VBScript Regular Expressions 5.5 to search a string for a Unicode sequence …
' --------------------------------------------------------------------- ' RegExFindUnicode ' Search an input string for a regular expression pattern such as \178 ' If found, substitute the corresponding Unicode character ' Returns: the input string with the code sequence replaced with a Unicode char ' --------------------------------------------------------------------- Function RegExFindUnicode(pattern As String, search As String) As String Dim oRegExp As RegExp Dim oMatch As Match Dim oMatches As MatchCollection Dim result As String Set oRegExp = New RegExp oRegExp.pattern = pattern oRegExp.IgnoreCase = True oRegExp.Global = True If (oRegExp.Test(search) = True) Then Set oMatches = oRegExp.Execute(search) ' Execute search If 0 < oMatches.Count Then Set oMatch = oMatches(0) ' Get everything up to code result = Left(search, oMatch.FirstIndex) ' Convert the code to a character Dim length As Integer length = Len(oMatch.Value) result = result & ConvertUnicodeToChar(oMatch.Value) ' Add anything remaining after the code result = result & Mid(search, 1 + length + oMatch.FirstIndex) End If 'For Each oMatch In oMatches ' Iterate Matches collection. ' result = result & "Match found at position " ' result = result & oMatch.FirstIndex & ". Match Value is '" ' result = result & oMatch.Value & "'." & vbCrLf 'Next Else result = "String Matching Failed" End If RegExFindUnicode = result End Function
Test the Regular Expression Function
Here's a subroutine to test the above function …
Sub TestRegEx ()
Const Pattern As String = "\\[0-9]{3,4}"
Const Search As String = "Area = 100m\178"
Dim result As String
result = RegExFindUnicode (Pattern, Search)
Debug.Print "Searched for '" & Pattern & "' in '" & Search & "'"
Debug.Print "Result '" & result & "'"
End Sub
Regular Expression Help & References
Regular expressions have been around for a long time — several decades. The syntax is challenging, however. You may feel that you need assistance. Searching the web for regular expressions vba will find some results. There are also books available, if you want to browse in peace and quiet away from your keyboard.
Some sites let you experiment with regular expressions. For example, Regular Expression Test Page.
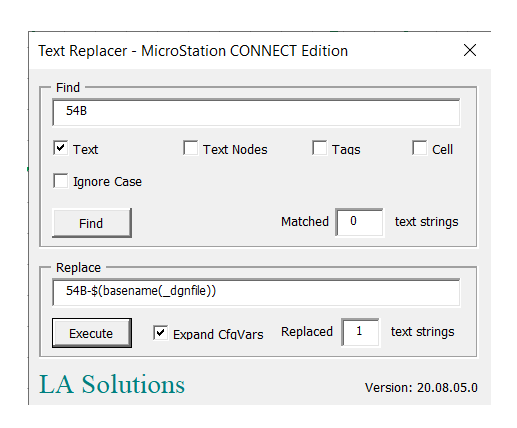
Text Search & Replace Tool

This tool uses regular expressions to analyse text in MicroStation
TextElements, TextNodeElements, TagElements and CellElements.
Type a regular expression into the Find box, then …
- Choose what you want to find …
- text in text elements
- text in text node elements
- text in tag elements
- text contained in cell elements
- Choose whether to ignore case when matching text
Press the Find button. The tool scans the active DGN model for elements that might contain text. For each text element that it locates, it extracts its text and tests it using your regular expression. The number of matches is shown next to the Find button.
The tool pops the Search Results dialog that shows the Element IDs and type description of each matching element …
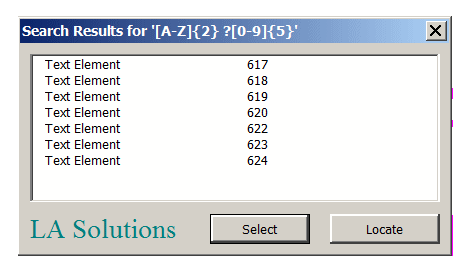
The Search Results dialog shows a list of matching elements.
Select a row in the list and click the Locate button to instruct MicroStation to focus on the selected element in view 1.
Click the Select button to instruct MicroStation to add all elements in the list to a selection set.
Selection Sets and Fences
This text search tool is sensitive to user-defined selections and fences. The algorithm implemented here is …
- If a selection set is active, search only those selected elements
- Otherwise, if a fence is active, search only the contents of the fence
- If neither a selection set nor a fence is active, search the active DGN model
Replace Text
If you want to replace text, then take these additional steps …
- Type a replacement text string into the Substitute box
- Optionally, click the Expand CfgVars button
Press the Execute button. The tool scans the active DGN model as before. This time, in addition to finding text that matches your regular expression, it also substitutes the replacement text for each match.
If the Expand CfgVars is checked, then the tool will expand any configuration variable it finds in the
replacement text.
For example, if the replacement text includes $(_dgnfile) it expands that to the name of the active
DGN file.
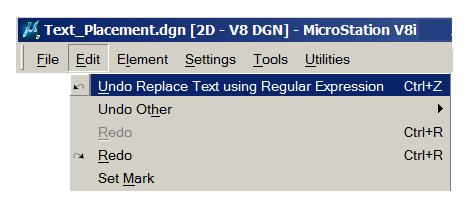
This operation is undoable. The command is stored in MicroStation's command buffer, so you can choose Edit|Undo to reverse the changes …
Questions
Post questions about MicroStation programming to the MicroStation Programming Forum.

Download the Text Replacer Tool
You can download the Text Replacer MVBA project.
The project includes the MVBA project TextReplacer.mvba
and an example DGN file with a few lines used to test the project.
- Unpack the ZIP archive to a suitable location, such as
..\Organization\Standards\macros - Start the tool with the MicroStation keyin
vba run [TextReplacer]modMain.Main - The Text Replacer dialog opens
Questions
Post questions about MicroStation programming to the MicroStation Programming Forum.