Questions similar to this appear on the Be Community Forums. This problem appeared in the MicroStation Forum. Users want to be able to find by name a shared or normal cell. That function is already provided by MicroStation's Select by Attributes tool (menu Edit|Select by Attributes). However, that tool obliges you to provide the exact cell name: you can't provide a wild-card (e.g. search for "Cell*").
Q How do I …
- find a named cell using VBA?
- find a named cell with a wild-card using VBA?
- perform a wild-card comparison using VBA?
Select by Attribute Tool
A MicroStation includes a Select by Attributes tool. You can search for a named normal or shared cell using this tool — you don't need VBA.
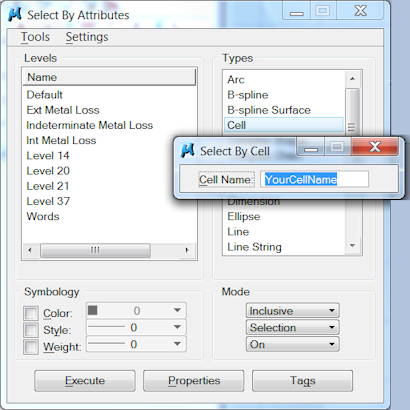
However, that tool may not provide some particular feature, or you just like writing VBA code. In that case, look at this VBA FindCell example and adapt the code to your needs.
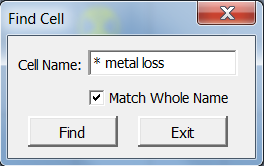
Find Cell
A
MicroStation includes a scanning engine that is used for many purposes. It's available to you in VBA
as the ModelReference.Scan method. You specify what you want to search for (e.g. cells) through
the ElementScanCriteria object.
The methodology of scanning a model is straightforward …
- Decide what you want to find
- Create an
ElementScanCriteriaobject and specify your filter requirements - Invoke the
ModelReference.Scanmethod - Enumerate the elements that pass the scan criteria
This could be, for example, elements on a certain level, elements of a certain type, or some combination of those criteria
Enumeration provides you with a list of elements, each of which has already passed the test you
imposed with your scan criteria. So, if you specified a level filter, you know that each element received from
the enumerator belongs to one of the levels specified. If your scan criteria requested only normal or shared cell elements,
then each element returned by the enumerator will be a CellElement or SharedCellElement.
Scan for Cells
There are a number of scanning examples provided in the VBA help. Search help for scan criteria or scan to find them.
Here's an example that searches for cells: copy this code into a module in the VBA editor and
vba run ScanCells …
' Scan for Normal and Shared cell elementsPublic Function ScanCells () As Boolean ScanCells = False Dim oCriteria As New ElementScanCriteria Dim oEnumerator As ElementEnumerator oCriteria.ExcludeAllTypes' Scan for normal cellsoCriteria.IncludeType msdElementTypeCellHeader' Scan for shared cellsoCriteria.IncludeType msdElementTypeSharedCell Set oEnumerator = ActiveModelReference.Scan(oCriteria) Do While oEnumerator.MoveNext' Normal or Shared cell is referenced by oEnumerator.CurrentScanCells = True Loop End Function
Scan for Named Cells
If you want to look for a cell where you know the exact name of the cell, you can provide the name to the scanner …
' Scan for Normal and Shared cell elementsPublic Function ScanCells (ByVal name As String) As Boolean ScanCells = False Dim oCriteria As New ElementScanCriteria Dim oEnumerator As ElementEnumerator' Scan for named celloCriteria.IncludeOnlyCell name oCriteria.ExcludeAllTypes' Scan for normal cellsoCriteria.IncludeType msdElementTypeCellHeader' Scan for shared cellsoCriteria.IncludeType msdElementTypeSharedCell Set oEnumerator = ActiveModelReference.Scan(oCriteria) Do While oEnumerator.MoveNext' Normal or Shared cell is referenced by oEnumerator.CurrentScanCells = True Loop End Function
Scan for Named Cells with Wild-Card
What happens if you don't know the exact name of the cell,
or you want to find cells having names like "ABC"?
The ElementScanCriteria provides no string comparison methods,
so you must take another approach.
If you want to look for a cell where you don't know the exact name of the cell,
you can provide string with a wild-card.
By wild-card we mean something like "ABC*",
where the asterisk means 'zero or more characters'.
Then, examine each cell returned by the scanner,
and compare its name with your wild-card …
' Scan for cell elements with a wild-cardPublic Function ScanCells (ByVal wildCard As String) As Boolean ScanCells = False Dim oCriteria As New ElementScanCriteria Dim oEnumerator As ElementEnumerator' We can't use IncludeOnlyCell because it wants an exact cell name 'oCriteria.IncludeOnlyCell nameoCriteria.ExcludeAllTypes' Scan for normal cellsoCriteria.IncludeType msdElementTypeCellHeader Set oEnumerator = ActiveModelReference.Scan(oCriteria) Do While oEnumerator.MoveNext If (CompareCellNameWithWildCard (oEnumerator.Current.AsCellElement.Name, wildCard)) Then ScanCells = True End If Loop End Function
The question you're now asking is, "What do we write in CompareCellNameWithWildCard?"
VB and VBA have limited capability for matching strings.
You can use function StrComp to match a complete string,
and InStr to see if one string contains another.
But, for wild-card comparison, you're stuck.
Regular Expressions provide a solution!
Regular Expressions
Regular Expressions (RegExs) have been around for many years, but Microsoft included no regular expression functionality in VB or VBA.
However, Microsoft introduced a Regular Expression handler for VBScript, which you can use in your VB or VBA project. As you probably know, you can use ActiveX components in your VB code by adding a reference to the appropriate DLL or OCX. Read this Microsoft article How To Use Regular Expressions in Microsoft Visual Basic 6.0.
We need to add a reference to the Microsoft VBScript Regular Expressions 5.5. This is almost certainly already installed on your computer. In the VBA IDE, use menu Tools|References to pop the References dialog (these are Windows COM references, nothing to do with MicroStation reference files) …
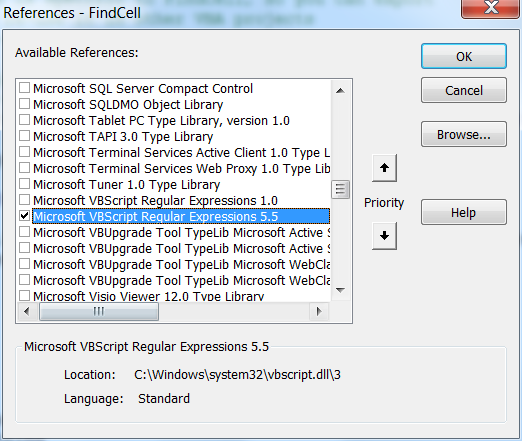
With that DLL referenced, you can now use the objects it provides.
These include the RegExp, Match and MatchCollection classes.
The purpose of this article is to show how to match a cell name with a wild-card,
so we won't go into the detail of Regular Expression: we'll just use what Microsoft provides …
' --------------------------------------------------------------------- ' CompareStringRegEx ' String matching function using Regular Expression handling. This ' uses the VBScript Regular Expressions mentioned in above. ' This won't work, or even compile, unless you have referenced the ' COM DLL mentioned in the note. ' ' This web site provide some background information about ' VBScript Regular Expressions: ' http://www.regular-expressions.info/vbscript.html ' ' Arguments: ' compare [String]: the string you want to compare ' matchString [String]: the string to compare with ' matchCase [Boolean]: True if you want a case-sensitive comparison ' ---------------------------------------------------------------------Public Function CompareStringRegEx(ByVal pattern As String, matchString As String, ByVal matchCase As Boolean) As Boolean CompareStringRegEx = False'Prepare a regular expression objectDim oExpression As New VBScript_RegExp_55.RegExp Dim oMatches As VBScript_RegExp_55.MatchCollection Dim oMatch As VBScript_RegExp_55.Match oExpression.IgnoreCase = Not matchCase oExpression.Global = True oExpression.pattern = pattern Set oMatches = oExpression.Execute(matchString) If (0 < oMatches.Count) Then CompareStringRegEx = True For Each oMatch In oMatches' In this example, we're not interested in individual matchesNext Else' No matchesEnd If End Function
Example VBA Project
The FindCell VBA Project is a complete example. It provides source code that uses both the MicroStation VBA scanner and the Microsoft Regular Expression classes. You can use the project as-is to find cells in your DGN models, or you can adapt the code to suit your needs.

Download the FindCell project,
which is in a ZIP archive.
Extract FindCell.mvba to a well-known location,
such as folder
\Bentley\Workspace\Standards\vba.
To run the application, keyin one of …
-
vba run [FindCell]modFindCell.FindCell -
vba run [FindCell]modFindCell.FindCell cell-name
The first keyin pops the FindCell dialog with an empty cell name. The second keyin pops the FindCell dialog with the cell name provided …

Press the Find button to locate a cell having the specified name. If found, View 1 is focussed on the cell, which is centred in the view. Pressing Find again takes you to the next instance of a cell that matches the name you provided.